Understanding Pack Dynamics: Wolf Behavior & Dog Interactions
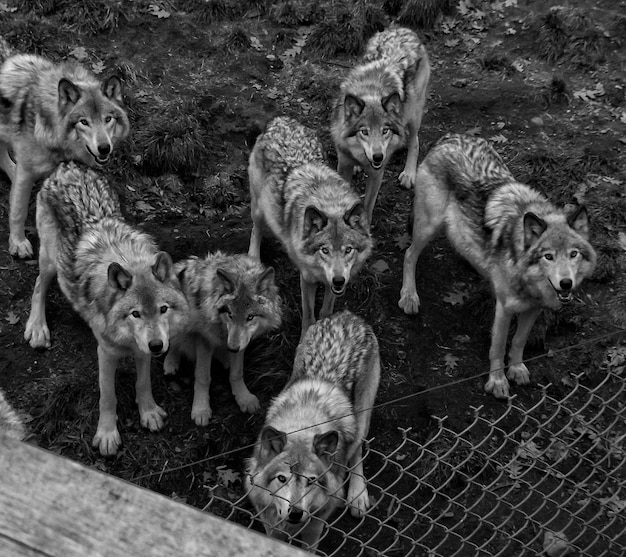

Understanding pack dynamics unveils the profound influence of wolf behavior on domestic dog interactions, shedding light on social structures, communication, and hierarchical roles that shape canine behavior.
Do you ever wonder why your dog behaves the way it does in social situations? The key to understanding canine social behavior may lie in understanding pack dynamics: how wolf behavior influences domestic dog interactions. By examining the social structures, communication methods, and hierarchical roles observed in wolf packs, we can gain valuable insights into the behavior of our furry friends.
Decoding Wolf Pack Dynamics: An Overview
Wolf packs have been studied for decades, providing researchers with a wealth of information about social behavior and communication. These highly organized groups are characterized by complex relationships and clear hierarchies, all of which contribute to the survival and success of the pack. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for grasping the roots of domestic dog behavior.
Examining the roles within a wolf pack and how these interactions translate into the behavior of our domestic dogs can offer valuable insights. From communication methods to hierarchical structures, wolf behavior profoundly influences how dogs interact with each other and with humans.
Hierarchical Structure in Wolf Packs
In any wolf pack, there’s usually a clear hierarchy. The alpha pair, typically consisting of the most dominant male and female, leads the pack and makes important decisions. Other members have defined roles and responsibilities within this structure.
This hierarchical structure is essential for maintaining order and minimizing conflict within the pack. Each member understands their place and contributes to the overall well-being of the group.
Communication Methods in Wolf Packs
Wolves are masters of communication, using a variety of signals to convey messages within the pack. These signals include vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. Effective communication is necessary for coordinating activities, resolving conflicts, and maintaining social bonds.
Through howls, growls, postures, and even subtle shifts in body weight, wolves can express a wide range of emotions and intentions, helping to ensure the pack functions as a unified whole
- Vocalizations: Howls serve to signal presence, territory, and coordinate hunts.
- Body Language: Postures, facial expressions, and tail movements communicate dominance, submission, and playfulness.
- Scent Marking: Wolves use urine and feces to mark their territory and communicate information about their presence.
Ultimately, studying the organization of wolf packs offers a foundational understanding of social dynamics that extend to our canine companions. This basic understanding helps to provide a context to dogs’ behavior.

The Influence of Wolf Social Structure on Dog Behavior
Domestic dogs, while genetically distinct from wolves, still carry the legacy of their ancestors’ social structures. Understanding how wolf social dynamics translate into dog behavior provides valuable insights into why dogs behave the way they do.
By recognizing these connections, we can better understand and manage our dogs’ social interactions, leading to improved relationships and fewer behavioral issues.
Dominance and Submission
One of the key aspects of wolf social structure that influences dog behavior is the concept of dominance and submission. While not always as rigid as in wolf packs, dogs still exhibit these behaviors in their interactions with other dogs and with humans.
Understanding these roles can help you recognize and address any issues related to dominance aggression or submissive behavior in your dog.
Pack Mentality in Domestic Dogs
Dogs tend to view their human families as their “pack,” and they may exhibit behaviors that reflect this pack mentality. This can include loyalty, protectiveness, and a desire to please their human leaders.
Knowing how dogs perceive their social environment is vital for effective training, communication, and building a strong bond with your canine companion.
- Loyalty: Dogs show unwavering loyalty to their human “pack” members.
- Protectiveness: They may exhibit protective behaviors towards their families and territory.
- Desire to Please: Dogs often seek approval and praise from their human leaders.
Recognizing the carryover of wolf social structure into dog behavior allows owners to interpret their dogs actions from an informed perspective. Furthermore, owners are better equipped to engage in effective training which promotes healthier habits.
Communication Styles: Wolves vs. Dogs
Although dogs have evolved to communicate with humans, they still rely on many of the same communication methods used by wolves. By understanding these similarities and differences, we can improve our ability to communicate with our dogs and interpret their behavior.
Effective communication is critical for building trust and understanding between humans and dogs, leading to stronger relationships and fewer misunderstandings.
Verbal Communication
Both wolves and dogs use vocalizations to communicate with each other, but the range and frequency of these vocalizations may differ. Dogs, for example, tend to bark more than wolves, while wolves rely more on howls.
Understanding the nuances of these vocalizations can help you interpret your dog’s mood and intentions.
Non-Verbal Communication
Body language is a crucial component of communication for both wolves and dogs. Postures, facial expressions, and tail movements all convey important information about their emotional state and social intentions.
By paying close attention to your dog’s body language, you can gain valuable insights into their feelings and motivations.
- Postures: Dominant dogs may stand tall and assertive, while submissive dogs may crouch low to the ground.
- Facial Expressions: Lip licking, yawning, and whale eye (showing the whites of the eyes) can indicate stress or anxiety.
- Tail Movements: A wagging tail doesn’t always mean happiness; it can also indicate excitement or agitation.
By understanding how dogs’ communication styles are rooted in wolf behavior, we can improve our own comprehension of canine interactions. Greater understanding is paramount to improved relationships.
Instincts and Learned Behaviors in Dogs
While wolf behavior provides a valuable foundation for understanding dog behavior, it’s important to remember that dogs are also influenced by domestication and learning. Some behaviors are instinctual, while others are learned through experience and training.
Recognizing the interplay between instinct and learning is essential for effective dog training and management.
The Role of Genetics
Certain breeds of dogs are predisposed to certain behaviors due to their genetic heritage. For example, herding breeds like Border Collies have a strong instinct to herd, while retrieving breeds like Labrador Retrievers have a natural inclination to retrieve.
Understanding your dog’s breed-specific traits can help you tailor training and activities to suit their natural abilities.
The Impact of Environment
A dog’s environment and upbringing also play a significant role in shaping their behavior. Early socialization, training, and exposure to different experiences can all influence how a dog interacts with the world around them.
Providing a positive and enriching environment is crucial for promoting healthy behavior and well-being in dogs.
- Early Socialization: Exposing puppies to a variety of people, dogs, and environments during their critical socialization period (3-16 weeks) can help prevent fear and aggression later in life.
- Training: Obedience training can teach dogs valuable skills and provide mental stimulation.
- Enrichment: Providing opportunities for dogs to engage in natural behaviors, such as chewing, digging, and playing, can help reduce boredom and prevent behavioral problems.
Overall, the blending of predisposed instincts with learned behaviors, refined through the dog’s lifetime, defines the actions of dogs. Owners should consider these components when trying to understand their actions.
Applying Wolf Pack Knowledge to Dog Training
By understanding the principles of wolf pack dynamics, you can apply this knowledge to your dog training efforts. A deeper understanding of canine behavior can assist in building a stronger, more trusting bond.
Using these insights to better understand training approaches fosters communication between owner and dogs. This creates a richer learning environment and improved obedience.
Establishing Leadership
Dogs naturally look for a leader within their pack, whether it’s a human or another dog. By establishing yourself as a confident and consistent leader, you can earn your dog’s respect and cooperation.
Leadership isn’t about being dominant or aggressive; it’s about providing clear guidance and setting boundaries.
Positive Reinforcement Techniques
Positive reinforcement involves rewarding desired behaviors with praise, treats, or toys. This approach is more effective than punishment-based methods, as it encourages dogs to repeat the behaviors you want to see.
By focusing on positive reinforcement, you can build a strong and trusting relationship with your dog that is based on mutual respect and understanding.
- Rewards: Use high-value treats or toys to motivate your dog during training sessions.
- Consistency: Be consistent with your commands and expectations.
- Timing: Reward your dog immediately after they perform the desired behavior.
Incorporating knowledge about pack dynamics can reshape our approach to training, fostering a deeper alignment with canine instincts. The new focus on trust and positive reinforcement leads to improved outcomes.
Addressing Behavioral Issues Through Understanding Pack Dynamics
Many behavioral issues in dogs, such as aggression, anxiety, and excessive barking, can be rooted in misunderstandings of pack dynamics. By addressing these issues from a pack-oriented perspective, we can develop effective solutions.
The root causes of many common behavioral challenges are misaligned perceptions of social hierarchy and appropriate interaction within a “pack.” A pack oriented perspective enables a deeper comprehension of underlying issues.
Aggression Towards Other Dogs
Aggression towards other dogs may stem from a dog’s attempt to establish dominance or protect their territory. By understanding the underlying motivations, you can take steps to manage and redirect this behavior.
Consulting with a professional dog trainer or behaviorist can provide valuable guidance and support.
Separation Anxiety
Separation anxiety can occur when a dog feels insecure or abandoned when left alone. Addressing this issue may involve creating a sense of security and independence for the dog.
Gradual desensitization and counter-conditioning techniques can help alleviate separation anxiety.
- Create a Safe Space: Provide your dog with a comfortable and secure place to retreat when you’re away.
- Gradual Desensitization: Gradually increase the amount of time you leave your dog alone.
- Counter-Conditioning: Associate your departure with positive experiences, such as a tasty treat or a fun toy.
Recognizing the influence of pack dynamics on behavior enables owners to tackle issues with a refined focus on the dog’s social needs. With patience, clear communication, and the right training techniques, many behavioral problems can be effectively managed.
| Key Concept | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🐺 Pack Hierarchy | Wolves and dogs establish social order with dominant and submissive roles. |
| 🗣️ Communication | Canines use vocals, body language, and scent to interact with each other. |
| 🧬 Instinct vs. Learning | Dog behavior mixes genetics with experiences and training. |
| 🐾 Training | Understanding pack dynamics can enhance training techniques and strengthen relationships.. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
Wolf pack structures inform canine social behaviors, impacting interactions and hierarchy perceptions within domestic dog groups. Dogs use wolf behavior to understand social positions.
▼
The alpha is often the leader, usually a breeding pair that guides and protects the pack. The alpha pair makes crucial decisions regarding resources and safety.
▼
Wolves communicate through vocalizations (howls, growls), body language, and scent marking. These help to coordinate activities, express emotions, and maintain the group’s territory.
▼
Yes, knowledge of wolf social structures helps owners establish leadership using non-domineering methods, and use positive reinforcement that aligns with canine’s instinctual understandings.
▼
Domestication modifies genetic predispositions, environment, and social experiences. Breeds are bred to certain behaviors, while also allowing for learned adjustments to socialization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the intricate dynamics of wolf packs provides a profound insight into the behavior of our domestic dogs. The echoes of ancestral social structures, communication methods, and hierarchical roles resonate in our dogs' interactions with each other and with us. By recognizing these connections, we can enhance our training techniques, address behavioral issues more effectively, and ultimately, foster a deeper and more harmonious relationship with our canine companions.





